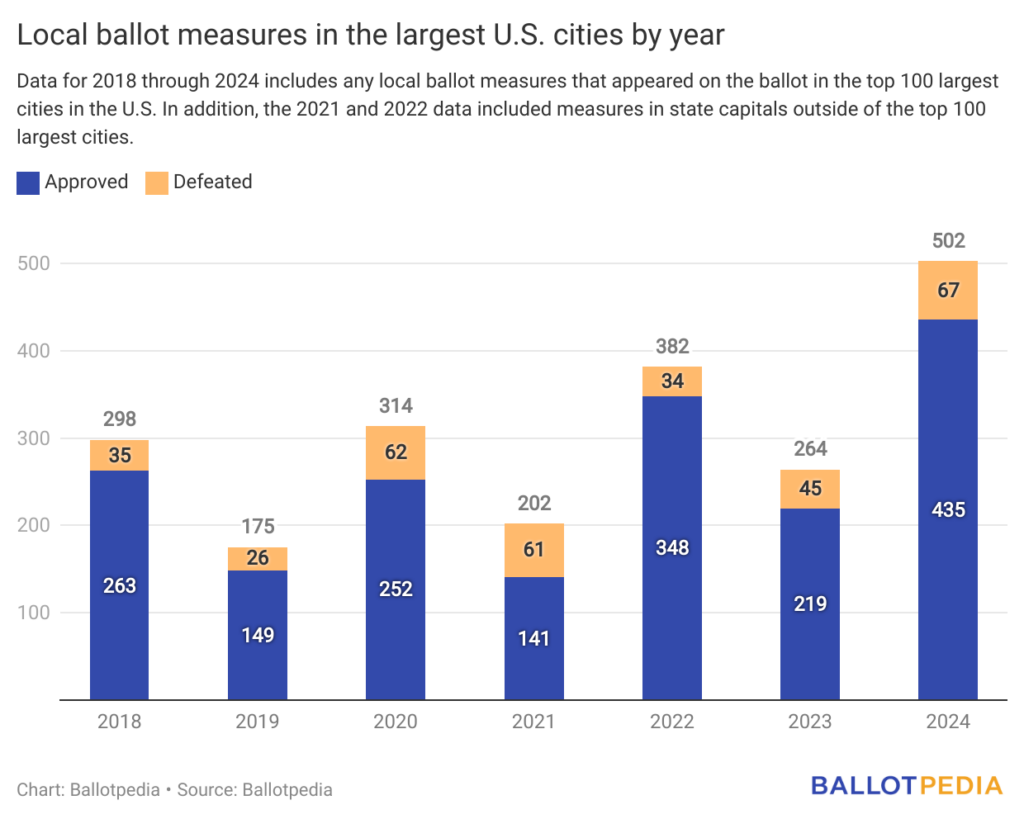
In 2024, Ballotpedia covered local measures that appeared on the ballot for voters within the top 100 largest cities in the U.S. and in the state capitals not among the 100 largest cities. There were 502 local measures across 37 states on the ballot for voters in the top 100 largest cities and state capitals in the U.S. in 2024.
Since 2018, the total number of local ballot measures has shown a consistent trend of higher totals in both even and odd-numbered years. The number of local ballot measures decided in top-100 cities was 298 in 2018, 314 in 2020, 382 in 2022, and 502 in 2024. The average percentage increase in the total number of local ballot measures across even years is approximately 19.5%, or an increase of about 70 measures per year.
The number of local ballot measures appearing on ballots in top-100 cities has also increased across odd years with 175 measures decided in 2019, 202 in 2021, and 264 in 2023, an increase of about 23% each year.
Of the 502 measures on the ballot in 2024, 435 (86.7%) were approved, and 67 (13.3%) were defeated.
Of the 502 local ballot measures within the top-100 cities and state capitals in 2024, 28 (5.58%) were citizen-initiated ballot measures. Initiatives are placed on the ballot through signature drives. The remaining 474 (94.42%) were referred to the ballot by local legislative bodies, such as county boards, city councils, school boards, and special district boards.
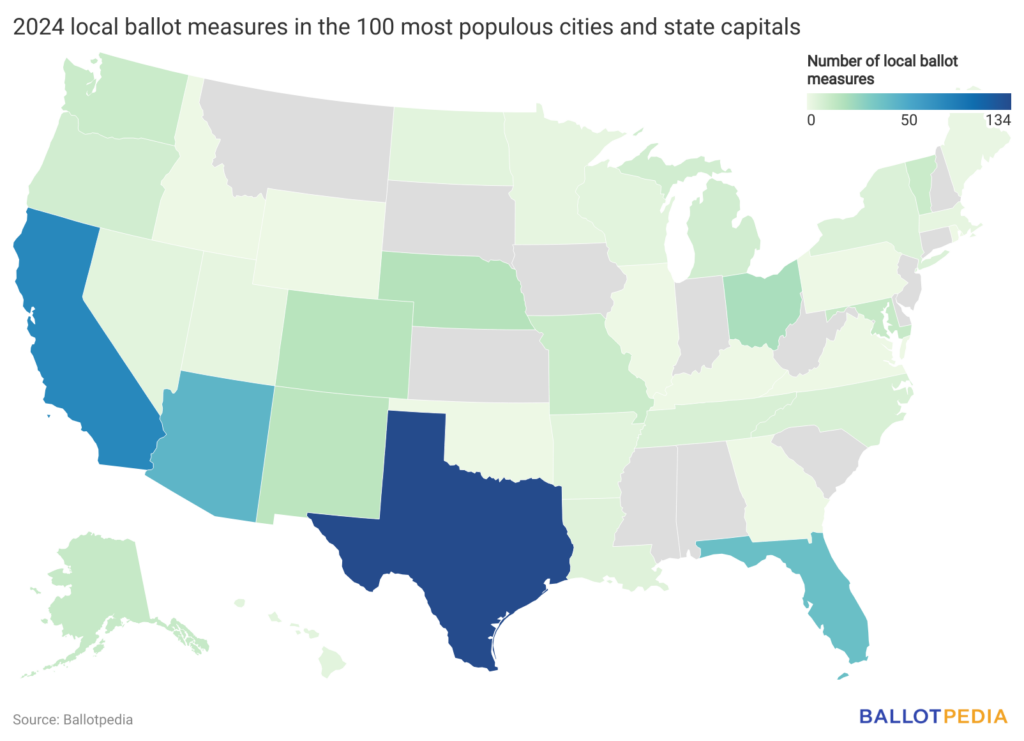
Among the top 100 largest cities, Texas (134 measures - 36.69%), California (79 measures - 15.74%), and Arizona (43 measures - 8.57%) were the three states with the most local measures covered.
The measures addressed a variety of topics. The most common topics of local ballot measures in 2024 were bond issues, taxes, and measures relating to local and school budgets, governance, and public officials. There were 145 local ballot measures that proposed the issuance of bonds in the top 100 largest cities and capitals in 2024 (including city, county, and school district bonds). The measures proposed a total of $38.55 billion in bonds. Voters approved 122 of the measures amounting to $31.46 billion. Voters rejected 23 ballot measures amounting to $7.09 billion.
Notable measures addressed abortion, wages, electoral systems, and election date changes.
Local abortion measures
Voters in San Francisco approved Proposition O, prohibiting the city from investigating or prosecuting an individual for seeking reproductive care and declared that San Francisco shall "serve as a safe and welcoming place for patients seeking reproductive health care, to protect the rights of pregnant persons to bodily autonomy and control over their private medical decisions, and to safeguard confidential health information between patients seeking access to reproductive health care and their providers."
Voters in Amarillo, Texas, defeated a measure that would have designated the city as a Sanctuary City for the Unborn and enacted local restrictions on abortion.
Wages
Voters in Glendale, Arizona, rejected Proposition 499, which would have provided for a local minimum wage of $20.00 per hour for hotel and event center workers. Voters in Long Beach, California, approved a measure to increase the minimum wage for qualifying hotel workers from $17.55 per hour to $29.50 per hour by July 2028.
Ranked-choice voting
Voters in Richmond, California, Oak Park, Illinois, and Washington, D.C., adopted measures to enact ranked-choice voting. Voters in Peoria, Illinois, adopted a measure advising the local government to enact ranked-choice voting.
Changes to election dates
Voters in St. Paul, Minnesota adopted a measure to change city elections to be held in presidential election years rather than odd-numbered years.
To read Ballotpedia's 2024 analysis of the 2024 local ballot measures in the largest U.S. cities and state capitals, click here.



