Welcome to Documenting America’s Path to Recovery, where we track the status of reopening in all 50 states. Today we look at Florida’s move into Phase 3 of reopening, new guidance for nursing home visitations in Missouri, travel restrictions, and more. Want to know what happened yesterday? Click here.
The next 72 hours
What is changing in the next 72 hours?
- Indiana (Republican trifecta): Gov. Eric Holcomb (R) announced on Sept. 23 that Indiana would move to Phase 5 of reopening on Sept. 26. In Stage 5, restaurants, bars, nightclubs, gyms, and fitness centers can operate at full capacity. Events with more than 500 participants or attendees will need to receive the approval of local health departments by submitting a written plan addressing social distancing measures and increased sanitation at least 14 days in advance of the event.
- Nevada (Democratic trifecta): At 11:59 p.m. on Sept. 27, bars in Clark and Elko counties will be permitted to reopen. Clark and Elko are currently the only two counties in the state where bars are closed.
Since our last edition
What is open in each state? For a continually updated article on reopening status in all 50 states, click here.
- Connecticut (Democratic trifecta): Gov. Ned Lamont (D) announced the state is targeting Oct. 8 to move to the third reopening phase. Phase 3 will allow businesses like restaurants and barbershops to operate at 75% capacity. Outdoor event venues (like amphitheaters and racetracks) and indoor performing arts venues will be able to operate at 50% capacity. Private indoor gatherings of up to 25 people and outdoor gatherings of up to 150 people will be allowed.
- Florida (Republican trifecta): Gov. Ron DeSantis (R) announced on Sept. 25 that Florida would enter Phase 3 of reopening effective immediately, allowing bars and restaurants to operate at full capacity. The order overrides local ordinances unless cities can justify bar or restaurant closures on health or economic grounds.
- New Hampshire (divided government): On Sept. 25, Gov. Chris Sununu (R) announced he would ease restrictions on indoor dining on Oct. 1, allowing restaurants to move tables closer than six feet apart if barriers separate them.
- New Jersey (Democratic trifecta): Gov. Phil Murphy (D) extended the state’s coronavirus public health emergency order for 30 more days.
|
Daily feature: Travel restrictions
Every Friday, we take a closer look at the restrictions governors and state agencies have placed on interstate travelers, including a recap of the week’s travel-related news. To see our full coverage of travel restrictions enacted in response to the coronavirus pandemic, click here.
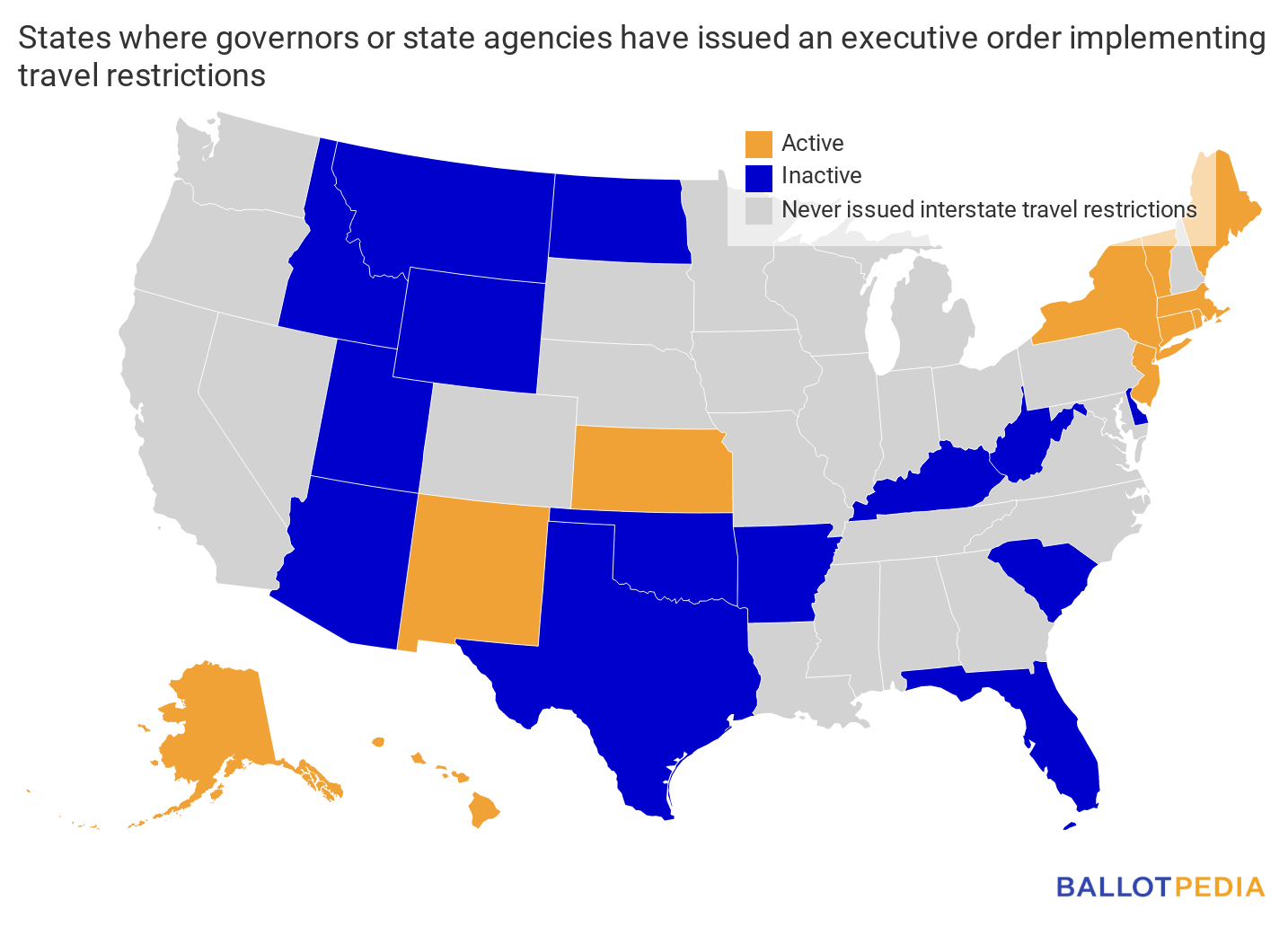
Overview
To date, 25 states issued at least one executive order restricting interstate travel. Of the 25 executive orders governors or state agencies issued restricting out-of-state visitors, at least 14 have been rescinded. Eleven states have active travel restrictions.
Weekly recap
- On Sept. 23, Maine Gov. Janet Mills (D) announced that Massachusetts travelers entering Maine would no longer be required to test negative or quarantine for 14 days. Other exempt states include New Hampshire, Vermont, Connecticut, New Jersey, New York, and Massachusetts. Travelers from all other states must be able to present a recent negative COVID-19 test at the request of the state or self-quarantine for 14 days upon arrival in Maine.
- On Sept. 23, New Mexico Gov. Michelle Lujan Grisham (D) added Colorado, Oregon, and Rhode Island to the list of high-risk states. Travelers from high-risk states must self-quarantine for 14 days upon arrival in New Mexico. Michigan and Hawaii were moved from high-risk to low-risk, exempting travelers from those states from the quarantine requirement.
- On Sept. 22, Govs. Ned Lamont (D-Conn.), Phil Murphy (D-N.J.), and Andrew Cuomo (D-N.Y.) announced that Arizona, Minnesota, Nevada, Rhode Island, and Wyoming had been added to the tristate quarantine list, which includes 33 states plus Guam and Puerto Rico.
- On Sept. 19, the Massachusetts Department of Public Health removed Wyoming from its list of low-risk states. Travelers from Wyoming must self-quarantine for 14 days upon arrival in Massachusetts.
Additional activity
In this section, we feature examples of other federal, state, and local government activity, private industry responses, and lawsuits related to the pandemic.
- On Sept. 22, a Washington, D.C. church filed suit against Mayor Muriel Bowser (D) in the U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia. In its complaint, the church challenges ongoing restrictions on physical gatherings in the District, and seeks the right to “gather for corporate worship free from threat of governmental sanction.” The church alleges the restrictions violate the Religious Freedom Act, and the First and Fifth Amendments. Rev. Thomas Bowen, director of Bowser’s Office of Religious Affairs, said, the pandemic “has placed us all in a tough situation, leading us to make adjustments to all aspects of our lives.” The case is assigned to Trevor McFadden, an appointee of President Donald Trump (R).
|


