Welcome to the Monday, April 24, Brew.
Here’s what’s in store for you as you start your day:
- Florida voters will decide whether to make their school board elections partisan
- Rate of election-related legislation enactment on par with 2022
- Ballotpedia’s Volunteer Fellows Program applications are open!
Florida voters will decide whether to make their school board elections partisan
Next year, Florida voters decide on a constitutional amendment that would allow for partisan school board elections.
On April 19, the Florida Senate gave final approval to House Joint Resolution 31 (HJR 31), a constitutional amendment that would establish partisan elections for seats on the state’s 67 school boards.
All 28 Republicans and Sen. Linda Stewart (D) voted in favor of the proposal. The chamber’s remaining 11 Democrats voted against it.
We told you about HJR 31 earlier this month after the House approved the proposal 79-34 along party lines.
With Senate approval, the proposal will now appear on the 2024 ballot, where it will need at least 60% of the vote to pass. The amendment would take effect for the 2026 school board elections if approved.
Florida’s proposal was one of a few proposed in legislatures this year. Lawmakers in Indiana and Kentucky introduced similar measures, but unlike Florida’s, neither advanced from their chamber of origin before their deadlines to be acted upon.
Florida is one of 41 states that hold nonpartisan school board elections where every candidate appears on the same ballot without party labels.
If voters approve the measure, Florida would become the fifth state to hold partisan school board elections exclusively, joining Alabama, Connecticut, Louisiana, and Pennsylvania, where candidates can choose to run under a specific party’s label.
The rules vary in Georgia, North Carolina, Rhode Island, South Carolina, and Tennessee. Some districts use partisan elections, while others use nonpartisan elections with differences typically based on specific state or local laws.
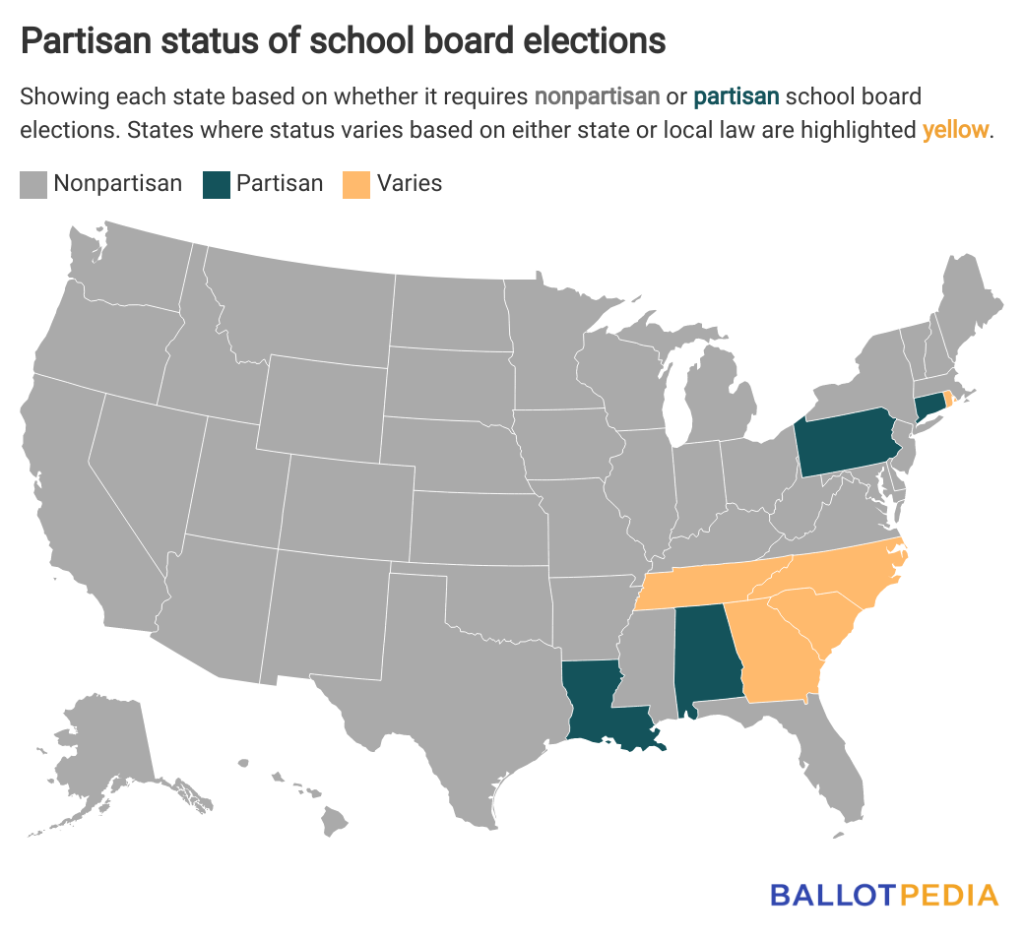
Tennessee most recently changed its school board election methods. In 2021, Gov. Bill Lee (R) signed into law a bill allowing county party committees to decide whether they want to use partisan or nonpartisan elections. Previously, all school board elections were nonpartisan.
Rate of election-related legislation enactment on par with 2022
State legislators have enacted roughly the same number of pieces of election-related legislation this year compared to the same point in 2022.
As of April 20, lawmakers nationwide have enacted 81 election-related bills this year. At this point in 2022, they had enacted 77.
Republican-sponsored legislation, up 31% compared to 2022, has primarily driven this year’s enactment rate. The number of enacted bills from Democratic sponsors is down 13%.
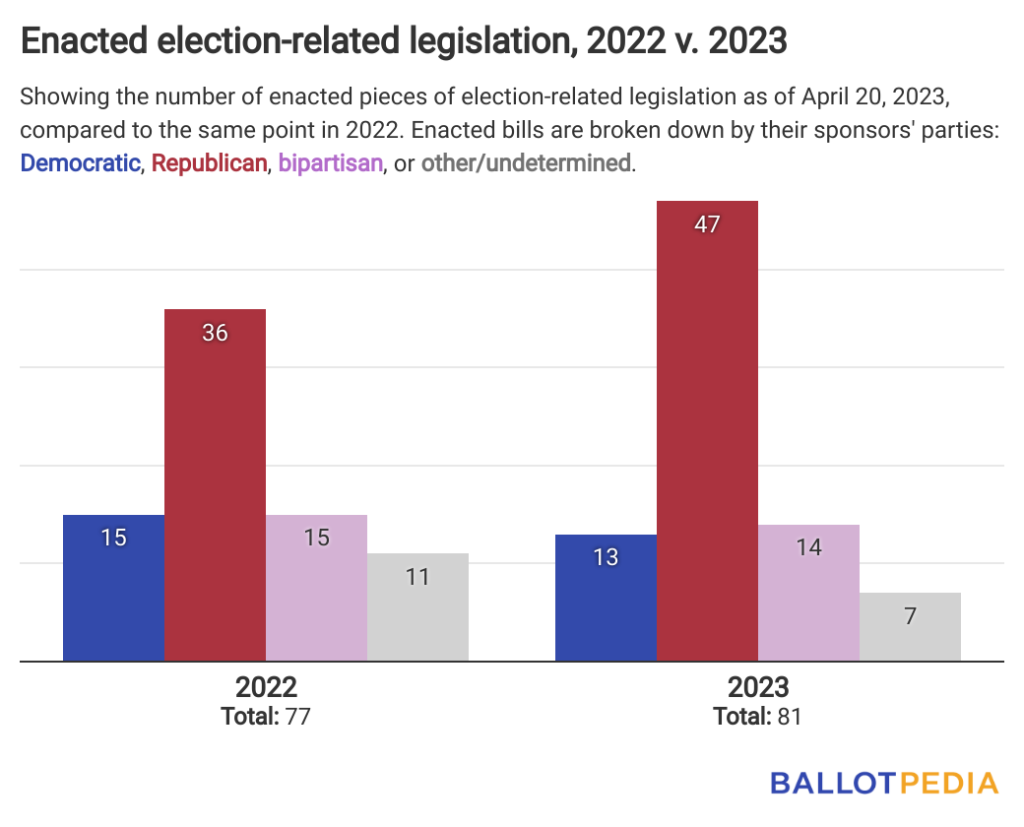
While the number of enacted bills so far in 2023 is similar to 2022, the subjects covered have been different.
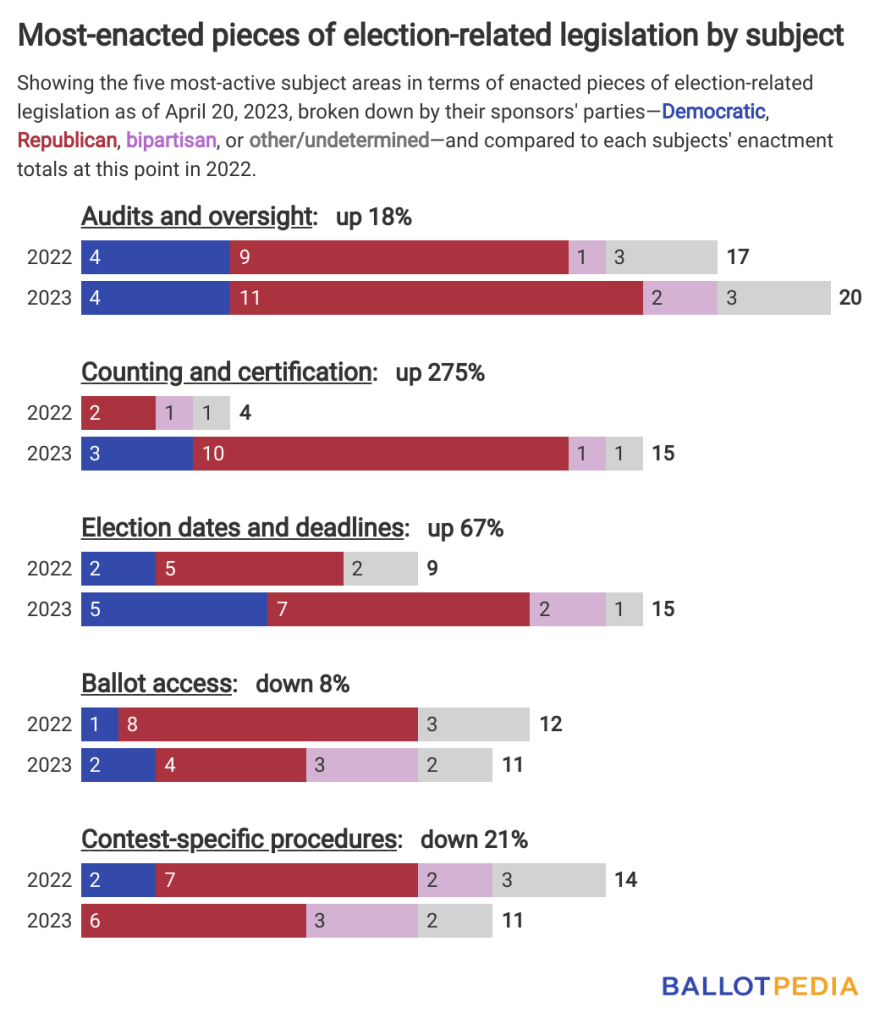
In terms of the number of enacted bills, the five most-active subjects so far this year are:
- Audits and oversight: 20 enacted, four from Democrats and 11 from Republicans.
- Rules or regulations regarding the auditing of final election results, publishing of election data, creating or modifying oversight authorities, or affecting poll observers;
- Counting and certification: 15 enacted, three from Democrats and 10 from Republicans.
- How ballots are processed, counted, canvassed, certified, and reported;
- Election dates and deadlines: 15 enacted, five from Democrats and seven from Republicans.
- Creating or altering election dates or things like voter registration, ballot access, and administrative deadlines;
- Ballot access: 11 enacted, two from Democrats and four from Republicans.
- How candidates, parties, or ballot measures qualify to appear on the ballot and regulations on their placement; and,
- Contest-specific procedures: 11 enacted, none from Democrats and six from Republicans.
- Rules or regulations relating to specific types of elections like municipal, primaries, and recalls.
The three most-active subject areas this year are also more active than they were a year ago. For example, the number of bills on counting and certification enacted so far in 2023 is up 275% compared to the number of similar bills enacted last year.
This year’s fourth and fifth most-active subject areas are less active than a year ago.
Here are a few examples of enacted bills in 2023:
- North Dakota: Senate Bill 2292, dealing with audits and oversight, created an offense for disturbing or obstructing a voter or election official on their way to or from a polling place. It also established that any individual, except a candidate, may be an election observer.
- Arkansas: House Bill 1487, dealing with counting and certification, requires that absentee ballots be delivered in a secure manner and adds several required data points. It also allows the public to view the canvassing of absentee ballots.
- New York: Senate Bill 1327, dealing with election dates and deadlines and other subjects, changes the deadline for a registered voter to change their address from 20 days before an election to 15 days before, among other deadline changes.
You can view a full list of enacted bills this year here. To stay up-to-date with the latest news in election-related legislation, subscribe to The Ballot Bulletin, our weekly newsletter that delivers the latest updates on election policy. Every week, we track legislative activity, big-picture trends, recent news, and in-depth data from our Election Administration Legislation Tracker.
Ballotpedia’s Volunteer Fellows Program applications are open!
Are you, or is someone you know, a politically-minded high school, college, or graduate student? If so, we’re excited to share the opening of our Summer 2023 Volunteer Fellows Program applications!
Ballotpedia Fellows have the opportunity to work closely with our staff and expand their knowledge of American politics through research of local officeholders and candidates on the ballot in upcoming elections.
Ballotpedia Fellows are passionate about politics and providing unbiased, factual information to voters! Fellows will gain valuable data analysis, communication, and research skills that can benefit them in future careers in politics, journalism, or other fields.
Don’t miss out on this unique opportunity to make a difference in American politics and earn a nationally recognized service honor from Ballotpedia!
Interested candidates can apply by filling out the application at the link below.

