Twenty-nine (29) legislative referrals were certified for statewide ballots in 2023 as of Jun. 15. Of that total, six received unanimous support from both parties; six received unanimous support from only Republicans; and 10 received unanimous support from only Democrats, which is higher than 2021 (4) and 2019 (5).
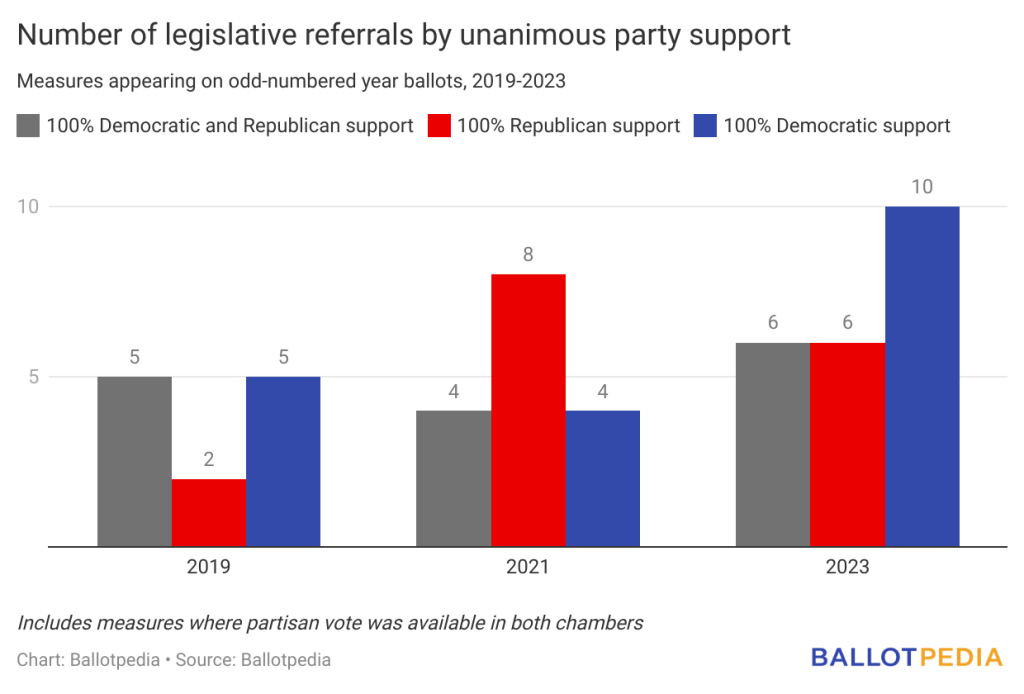
One measure in New York—where legislative constitutional amendments must be considered twice before heading to the ballot—received unanimous support from all members voting of both parties during both considerations of the bill.
The measures that received unanimous support from both parties include:
- Louisiana HB 166: Provides that the legislature may consider vetoed bills during a regular or extraordinary session rather than convening a separate veto session; clarifies that the governor’s deadline to act on a bill is based on the legislative session in which the bill was passed
- Louisiana HB 254: Repeals constitutional provisions establishing various state funds that are now inactive
- New York SB 8931: Excludes indebtedness for the construction or reconstruction of sewage facilities contracted before 2034
- Texas HJR 126: Establishes a right to farming, ranching, timber production, horticulture, and wildlife management in the state constitution
- Texas HJR 2: Authorizes the state legislature to make cost-of-living adjustments or other benefit enhancements to eligible annuitants of the teacher retirement system
- Texas SJR 75: Creates the Texas Water Fund to finance water projects
Ohio Issue 1 received no Democratic support. Issue 1 proposes requiring constitutional amendments to be approved by 60% of voters. It would also require petitions for initiated constitutional amendment to be signed by at least 5% of the electors in each of Ohio’s 88 counties, rather than the current requirement of 44 counties. Issue 1 received 95% of the vote of Republican legislators.
The measure that received the least Republican support was Colorado Proposition II with one Republican voting in favor of the amendment or 3% of all voting Republican legislators. Proposition II asks voters to either (1) allow the state to retain and spend revenue the state received above the estimated revenue generated from increases in taxes on cigarettes and tobacco and nicotine products in Proposition EE or (2) refund $23.65 million to distributors and wholesalers and reduce the tobacco tax rate by 11.53%.
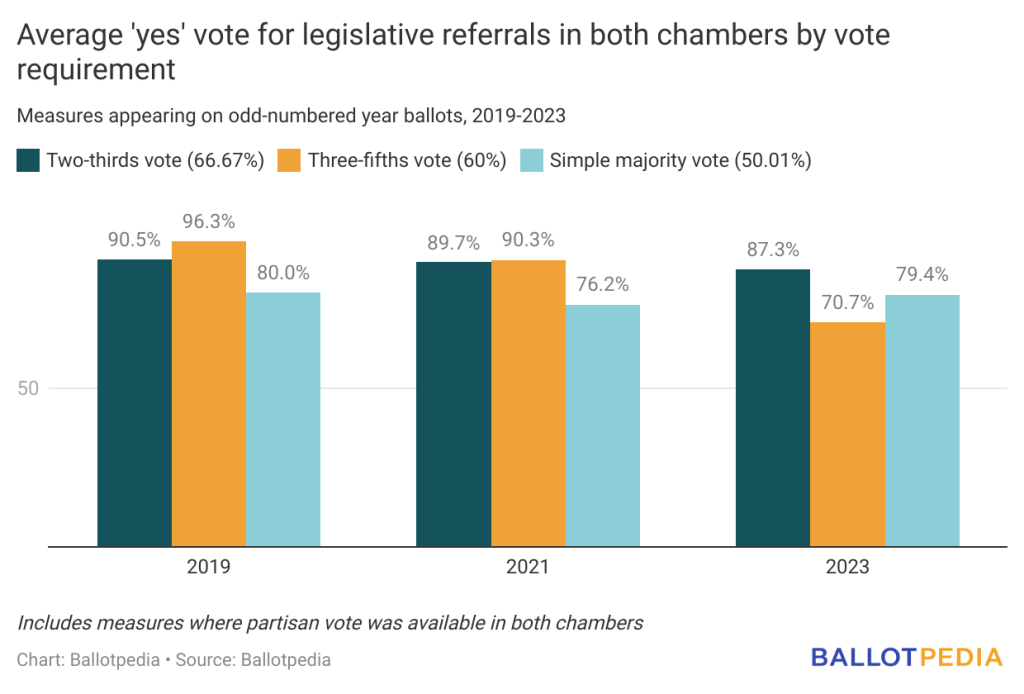
Of the 29 referrals, 21 measures required a two-thirds supermajority vote (66.67%); seven required a simple majority vote (50.01%); and one required a three-fifths supermajority vote (60%). The measures with a two-thirds vote requirement had the highest average ‘yes’ vote in both chambers with 87.3%. This is lower than the averages in 2021 (89.7%) and 2019 (90.5%).
The states with the two-thirds supermajority vote requirement are Louisiana and Texas. In Louisiana, Republicans have a supermajority in the House and the Senate by one vote in each chamber. The total number of votes needed in both chambers to place an amendment on the ballot is 96. The average number of votes received by a Louisiana legislative referral this cycle was 128.
In Texas, Republicans do not have a supermajority in either chamber; and therefore need 15 Democrats in the House and two Democrats in the Senate to vote with Republicans to meet the vote requirement. The total number of votes needed in both chambers to place an amendment on the ballot is 121. The average number of votes received by a Texas amendment this cycle was 150.
This year has so far exceeded the average number of referrals (28) on the ballot in odd-numbered year elections between 2011 and 2021.


