Tag: readability
-
At least 21 states have adopted laws addressing the readability of ballot measure language

Ballotpedia identified 21 states that have enacted laws addressing how legislators, secretaries of state, or other election officials write the question or description of a ballot measure. New York and North Dakota were the most recent states to do so in 2023. The New York State Legislature passed a law requiring that state ballot measure…
-
New York will require ballot measure questions to not exceed an eighth-grade reading level

Starting in 2024, New York will implement new language requirements for state ballot questions. On Nov. 17, 2023, Gov. Kathy Hochul (D) signed Senate Bill 1381 (SB 1381), which requires state ballot measure questions to be written using clear language and not exceed an eighth-grade reading level. In the Legislature, SB 1381 received a unanimous…
-
2023 statewide ballot measures written at graduate school reading level

The ballot language for the 41 statewide ballot measures on the ballot in eight states in 2023 is written at an average reading level of 19 (third-year graduate school reading level), which is up from 18 years in 2021. Ballotpedia identified five measures with a ballot summary, which is longer than the ballot title or…
-
The lowest and the highest readability scores for 2017-2022 ballot measures

Ballotpedia conducts an annual readability report analyzing what level of education voters would need to understand the ballot titles and summaries of statewide ballot measures using Flesch Reading Ease (FRE) and Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level (FKGL). Measurements used in calculating readability scores include the number of syllables, words, and sentences in a text. Other factors, such…
-
2022 statewide ballot measures written at graduate school reading level

The ballot language for the 140 statewide ballot measures on the ballot in 38 states in 2022 is written at an average reading level of 19 (graduate school reading level), up from 18 in 2021. Ballotpedia identified 66 measures with a ballot summary that was set to appear alongside the ballot question on the ballot.…
-
Statewide ballot measures written at first-year graduate school reading level
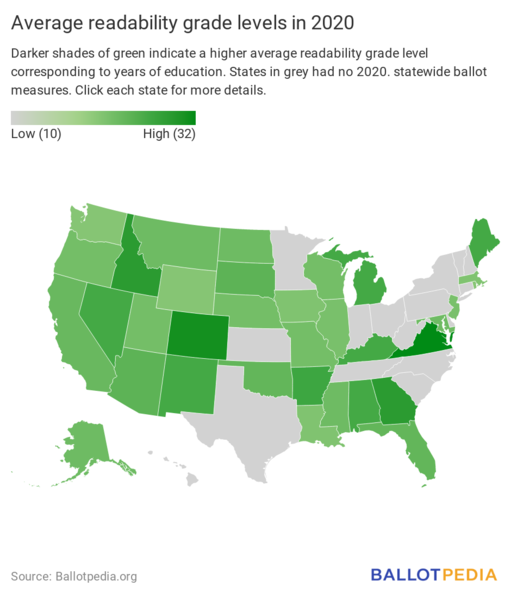
2020 ballot measure readability analysis: ballot language is written at an average reading grade level of 17 (first-year graduate school), down from between 19 and 20 in 2018 The average statewide ballot measure in 2020 is written at a reading grade level of 17, similar to the reading level in first-year graduate school. The 2020…

