Using data provided in the United States Census Bureau's 2024 American Community Survey estimates published in September 2025, and based on districts enacted after the 2020 census, there were 148 U.S. House majority-minority districts. This represented approximately 34% of the nation's 435 U.S. House districts.
A majority-minority district is a district in which a racial minority group or groups comprise a majority of the district's total population.
States may create majority-minority districts in order to prevent the dilution of minorities' voting strength in compliance with the Voting Rights Act of 1965. Section 2 of the Voting Rights Act mandates that no "standard, practice, or procedure shall be imposed or applied by any State or political subdivision to deny or abridge the right of any citizen of the United States to vote on account of race or color."
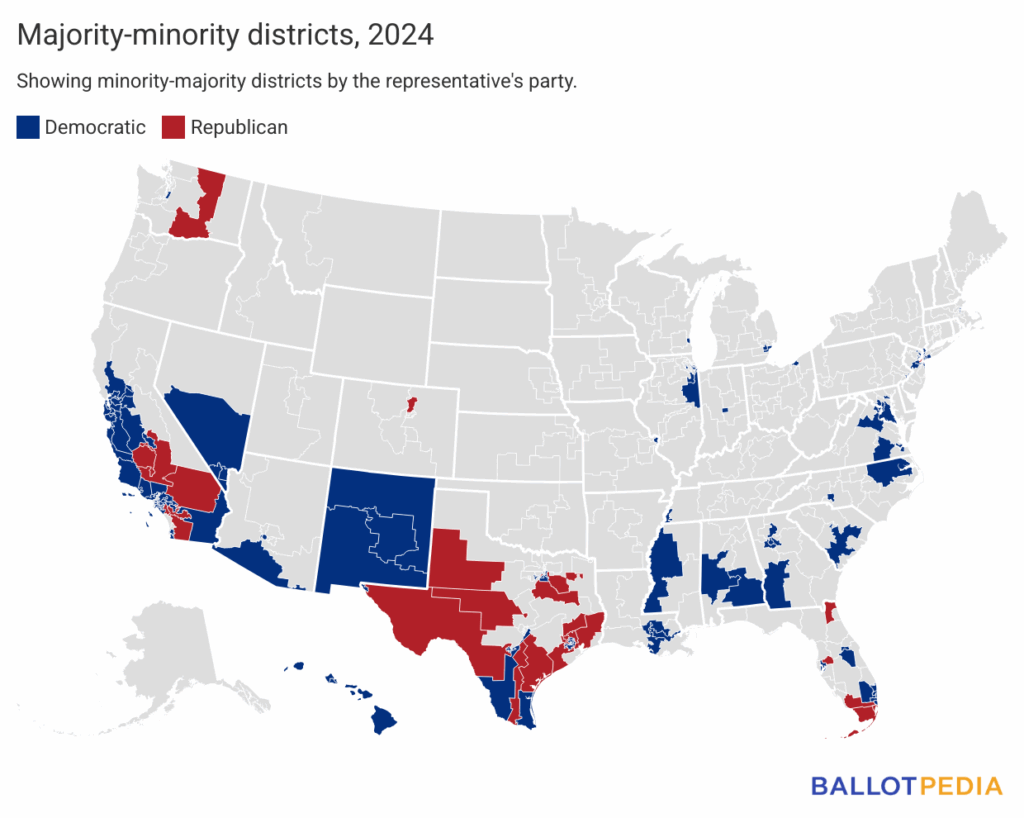
In 2024, the 148 majority-minority districts in the United States House of Representatives spanned 28 states, and 22 states had no majority-minority districts.
Here’s how the districts break down:
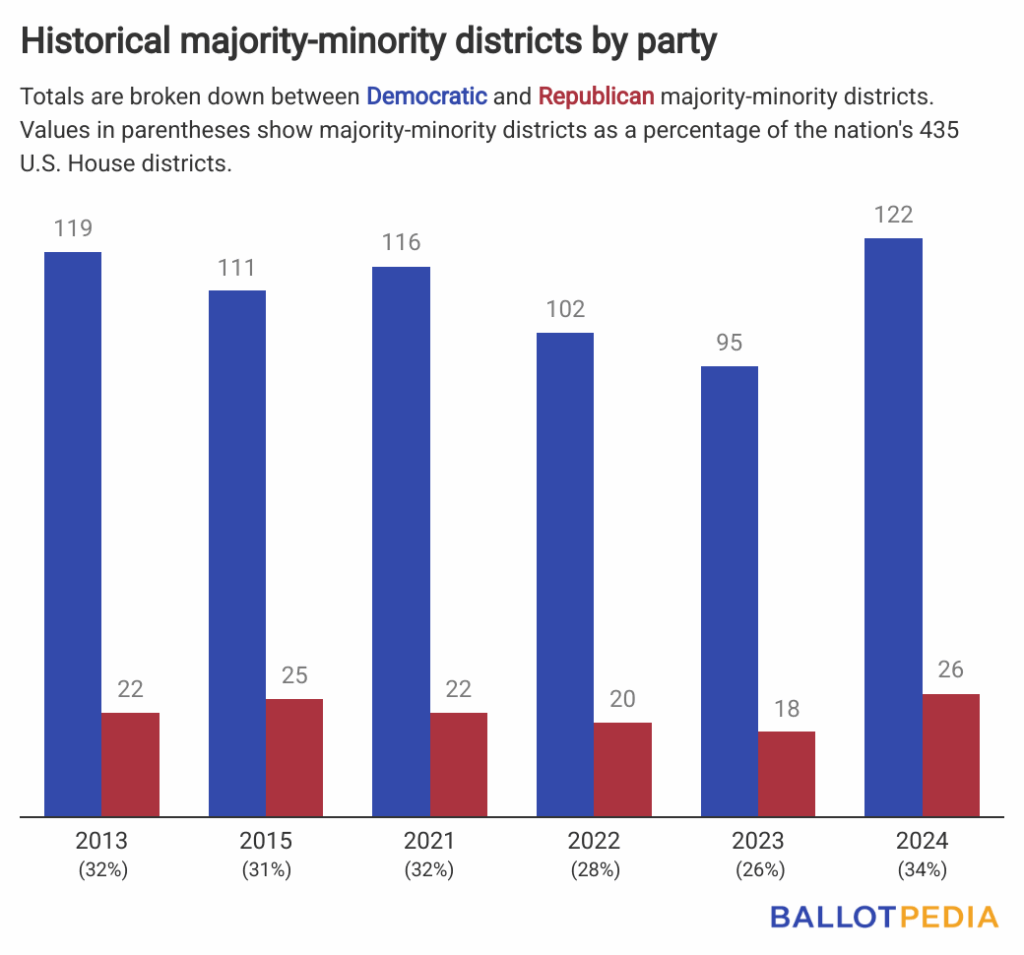
- Democrats represented 122 of the districts, and Republicans represented 26 of the districts in 2024.
- California had the most majority-minority districts with 44, or 85% of its 52 total congressional districts.
- Texas had the second-most with 24, or 63% of its 38 total congressional districts.
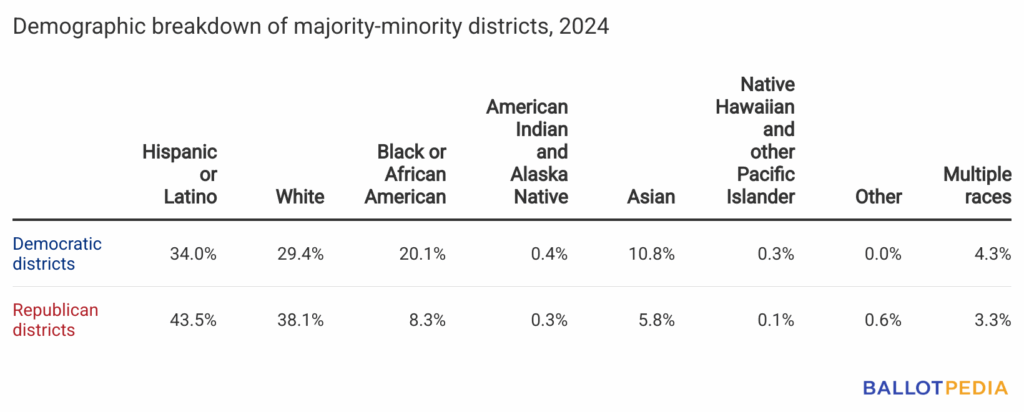
In both Democratic and Republican majority-minority districts, the largest racial group was Hispanic or Latino.
For Democrats, 122 is an estimated increase of six majority-minority districts since 2021. For Republicans, 26 is an estimated increase of four majority-minority districts.